| 一、细胞基本属性 | |||||
| 产品名称 | PSMC1 knockout HeLa cell line | ||||
| 产品货号 | IMKO-H010 | ||||
| 产品规格 | 1×106cells/T25或1mL冻存管 | ||||
| 储存及运输 | 干冰运输;储存在液氮中 | ||||
| 产品分类 | Hela细胞 | ||||
| 物种 | 人 | ||||
| 修饰基因 | PSMC1 | ||||
| 修饰类型 | 基因敲除 | ||||
| 转导方法 | CRISPR/Cas9 | ||||
| 克隆类型 | 纯化克隆 | ||||
| 细胞鉴定 | 通过遗传学方法确认PSMC1基因敲除 | ||||
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 | ||||
| 生长特性 | 贴壁生长 | ||||
| 培养体系 | 90%MEM+10% FBS+1%PS | ||||
| 传代比例 | 1:2至1:3 | ||||
| 传代周期 | 每周3次 | ||||
| 培养条件 | 气相:95%空气+5%二氧化碳;温度:37℃ | ||||
| 冻存条件 | 无血清冻存液,液氮储存 | ||||
补充内容 | PSMC1是一种编码蛋白质的基因,与一些疾病如Birk-Aharoni综合征和Bjornstad综合征相关联。在人体中,PSMC1编码的蛋白质是19S蛋白酶体复合物的19个基本亚基之一,这个复合物在蛋白质降解中起着重要作用。 最近的研究表明,PSMC1变异可以导致一种新的神经系统综合征。通过分子遗传学研究发现,PSMC1的双等位基因变异会影响真核蛋白酶体基本单位的一个组成部分,进而引起这种疾病。对果蝇的功能性研究验证了这种变异的致病性,显示PSMC1 Drosophila同源基因的消除会完全逆转表型效应。 | ||||
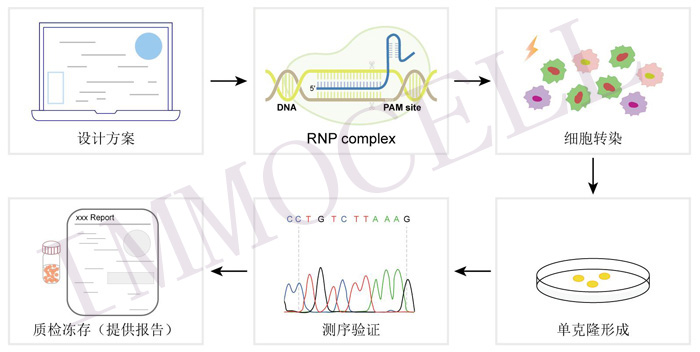
| 构建方法 |  | ||||
| PSMC1基因敲除细胞系的构建通常涉及的步骤 | 1.设计sgRNA(单指导RNA):选择目标PSMC1基因序列,并设计sgRNA用于精准敲除该基因。 2.选择适当的细胞系:选择适合的细胞系,通常选择易于转染和培养的细胞系。 3.转染sgRNA和Cas9:将设计好的sgRNA和Cas9基因导入目标细胞中,通常通过转染技术实现。 4.筛选敲除细胞系:利用细胞毒性筛选剂或选择性培养基对转染后的细胞进行筛选,筛选出成功敲除PSMC1基因的细胞系。 5.鉴定敲除细胞系:通过PCR、Western blot等技术验证PSMC1基因是否成功敲除,并确认细胞系中PSMC1蛋白的表达水平。 6.功能分析:对PSMC1敲除细胞系进行功能分析,比如观察其生长、增殖、代谢以及对特定刺激的反应等。 7. 维护和保存:维护敲除细胞系的培养,并进行合适的保存以备后续实验使用。 | ||||
| PSMC1基因的基本信息 | Species | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | GenBank Accession | Transcript |
Human (Homo sapiens) | PSMC1 | 5700 | NM_002802.3 | NP_002793.2 | |
| 关于基因 | Official Symbol | PSMC1 | |||
| Previous Symbol | PRS4 | ||||
| Official Full Name | Proteasome 26S Subunit, ATPase 1 | ||||
| Synonyms | P45, MOV-34, MGC13679 | ||||
| Location | 14q32.11 | ||||
| Gene Type | Protein Coding | ||||
| Uniprot ID | B4DR63, P49014, P62191, Q03527, Q6IAW0, Q6NW36, Q96AZ3 | ||||
| Pathway/Library | PSMC1 is involved in pathways related to protein degradation and cellular homeostasis. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome-mediated degradation and the assembly of the pre-replicative complex. | ||||
| Gene Summary | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes one of the ATPase subunits, a member of the triple-A family of ATPases which have a chaperone-like activity. This subunit and a 20S core alpha subunit interact specifically with the hepatitis B virus X protein, a protein critical to viral replication. This subunit also interacts with the adenovirus E1A protein and this interaction alters the activity of the proteasome. Finally, this subunit interacts with ataxin-7, suggesting a role for the proteasome in the development of spinocerebellar ataxia type 7, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] | ||||
相关问题
培养指南
-
hiPSC人诱导多能干细胞培养教程:在培养hiPSC细胞前,需准备好hESC/iPSC完全培养基配制和Matrigel铺板,hiPSC人诱导多能干细胞复苏操作,1. 将水浴锅预热至37℃;并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复···...
阅读详情 -
H9人胚胎干细胞培养条件与方法:1. 将水浴锅预热至37℃,并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复至室温(15~30℃);2. 取4 mL hESC/iPSC完全培养基,按照1:4000比例加入1 μL的hESC/iPSC Supplement C,···...
阅读详情 -
H1人胚胎干细胞培养指南:在培养h1干细胞之前,首先要准备好hESC/iPSC完全培养基配制, 铺板,H1人胚胎干细胞复苏步骤:1.将水浴锅预热至37℃;并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复至室温(15~30℃);···...
阅读详情 -
4T1细胞培养方法:小鼠乳腺癌4T1细胞培养基 90%DMEM+10% FBS+PS,生长条件:气相:95%空气+5%二氧化碳;温度:37℃,4T1细胞形态特征为上皮细胞样,贴壁生长,如果4T1细胞密度达80%-90%,即可进行传代培养,传代方法:1:2至1:3···...
阅读详情 -
常用人肝癌细胞系有哪些及如何选择:目前较为常用的几株人肝癌细胞系SMMC-7721、Bel-7402、MHCC97、HepG2、Hep3B、Huh-7 and PLC/PRF/5,那么人肝癌细胞株如何选择呢?一方面你可以查找相关的文献,另一方面可以考虑选择···...
阅读详情 -
HL-60细胞生长慢解决方法及如何养好:当HL-60细胞传代后生长速度慢且状态不佳时,可竖着培养直到培养基变黄,待细胞密度起来后,状态会有所好转,同时,若HL-60细胞状态很差,可采用半换液的方式:以T25瓶子为例,瓶子里有5m···...
阅读详情