| 细胞基本属性 | |||||
| 产品名称 | Caspase 1 knockout THP-1 cell line | ||||
| 产品货号 | IMKO-H036 | ||||
| 产品规格 | 1×106cells/T25或1mL冻存管 | ||||
| 储存及运输 | 干冰运输;储存在液氮中 | ||||
| 产品分类 | THP-1细胞 | ||||
| 物种 | 人 | ||||
| 修饰基因 | Caspase 1 | ||||
| 修饰类型 | 基因敲除 | ||||
| 转导方法 | CRISPR/Cas9 | ||||
| 克隆类型 | 纯化克隆 | ||||
| 细胞鉴定 | 通过遗传学方法确认Caspase 1基因敲除 | ||||
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 | ||||
| 生长特性 | 贴壁生长 | ||||
| 培养体系 | 90%MEM+10%FBS+1%PS | ||||
| 传代比例 | 1:2至1:3 | ||||
| 传代周期 | 每周3次 | ||||
| 培养条件 | 气相:95%空气+5%二氧化碳;温度:37℃ | ||||
| 冻存条件 | 无血清冻存液,液氮储存 | ||||
补充内容 | Caspase 1是一种特定的酶,属于半胱氨酸蛋白酶(caspase)家族,它在细胞凋亡(apoptosis)和炎症反应中扮演关键角色。Caspase 1的基因在人类中被称为CASP1,在鼠类中被称为Casp1。 细胞凋亡是一种程序性的细胞死亡过程,对于维持多细胞生物的内环境稳定和组织重塑至关重要。Caspase 1是凋亡过程中的一个早期启动者,它可以通过自身活化或者被其他Caspase酶激活,进而激活下游的Caspase酶,导致细胞结构的破坏和最终死亡。 此外,Caspase 1还参与炎症反应,它能够切割并激活炎症因子前体(如白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α),从而释放这些炎症介质,引发免疫反应。 | ||||
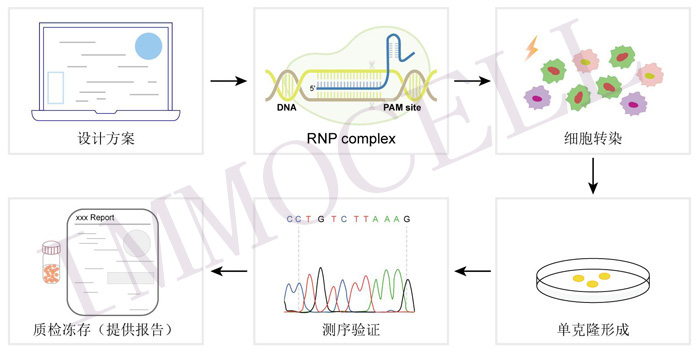
| 构建方法 |  | ||||
| Caspase 1基因敲除细胞系构建通常涉及的步骤 | 1.目标基因的确定:首先确定要敲除的Caspase 1基因(CASP1),并识别其在大肠杆菌中的编码序列。 2.设计sgRNA:设计小向导RNA(small guide RNA, sgRNA),它能够特异性地识别并绑定到Caspase 1基因的特定序列上。sgRNA的设计至关重要,因为它将决定基因敲除的效率和特异性。 3.构建CRISPR/Cas9系统:将sgRNA与Cas9蛋白以及适当的表达载体结合,构建CRISPR/Cas9系统。这个系统将用于在细胞中实现基因敲除。 4.将CRISPR/Cas9系统引入细胞:通过转染、电穿孔、脂质体介导的转染等方法将CRISPR/Cas9系统引入目标细胞中。 5.筛选和验证敲除细胞:通过PCR、测序等方法筛选出成功敲除Caspase 1基因的细胞。此外,可以通过功能实验(如细胞凋亡实验、炎症因子检测等)来验证敲除效果。 6.扩大培养和冻存:一旦筛选出敲除细胞,就需要将它们扩大培养以便进行后续的实验研究。同时,为了长期使用,还需要将细胞冻存起来。 7. 功能研究:在基因敲除细胞系中进行一系列的功能性实验,以研究Caspase 1基因敲除对细胞生物学功能的影响。 | ||||
| Caspase 1基因的基本信息 | Species | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | GenBank Accession | Transcript |
Human (Homo sapiens) | CASP1 | 834 | NP_150634 | NP_150634.1 | |
| 关于基因 | Official Symbol | CASP1 | |||
| Previous Symbol | CPP | ||||
| Official Full Name | Caspase-1 | ||||
| Synonyms | IL1BCICEP45Interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme | ||||
| Location | 11q22.3 | ||||
| Gene Type | Protein-coding | ||||
| Uniprot ID | B5MDZ1, P29466, Q53EY6, Q6DMQ1, Q6GSS3, Q6PI75, Q9UCN3 | ||||
| Pathway/Library | RAF/MAP kinase cascade | ||||
| Gene Summary | This gene encodes a protein which is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce 2 subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This gene was identified by its ability to proteolytically cleave and activate the inactive precursor of interleukin-1, a cytokine involved in the processes such as inflammation, septic shock, and wound healing. This gene has been shown to induce cell apoptosis and may function in various developmental stages. Studies of a similar gene in mouse suggest a role in the pathogenesis of Huntington disease. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012] | ||||
相关问题
培养指南
-
hiPSC人诱导多能干细胞培养教程:在培养hiPSC细胞前,需准备好hESC/iPSC完全培养基配制和Matrigel铺板,hiPSC人诱导多能干细胞复苏操作,1. 将水浴锅预热至37℃;并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复···...
阅读详情 -
H9人胚胎干细胞培养条件与方法:1. 将水浴锅预热至37℃,并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复至室温(15~30℃);2. 取4 mL hESC/iPSC完全培养基,按照1:4000比例加入1 μL的hESC/iPSC Supplement C,···...
阅读详情 -
H1人胚胎干细胞培养指南:在培养h1干细胞之前,首先要准备好hESC/iPSC完全培养基配制, 铺板,H1人胚胎干细胞复苏步骤:1.将水浴锅预热至37℃;并将Matrigel包被的6孔板,提前放置生物安全柜中约1小时恢复至室温(15~30℃);···...
阅读详情 -
4T1细胞培养方法:小鼠乳腺癌4T1细胞培养基 90%DMEM+10% FBS+PS,生长条件:气相:95%空气+5%二氧化碳;温度:37℃,4T1细胞形态特征为上皮细胞样,贴壁生长,如果4T1细胞密度达80%-90%,即可进行传代培养,传代方法:1:2至1:3···...
阅读详情 -
常用人肝癌细胞系有哪些及如何选择:目前较为常用的几株人肝癌细胞系SMMC-7721、Bel-7402、MHCC97、HepG2、Hep3B、Huh-7 and PLC/PRF/5,那么人肝癌细胞株如何选择呢?一方面你可以查找相关的文献,另一方面可以考虑选择···...
阅读详情 -
HL-60细胞生长慢解决方法及如何养好:当HL-60细胞传代后生长速度慢且状态不佳时,可竖着培养直到培养基变黄,待细胞密度起来后,状态会有所好转,同时,若HL-60细胞状态很差,可采用半换液的方式:以T25瓶子为例,瓶子里有5m···...
阅读详情